The healthcare framework in the United States is in a constant state of evolution, shaped by legislative acts, market dynamics, and societal demands. As 2024 unfolds, the nation is poised for significant changes in healthcare policies, which have diverse impacts on Americans depending on their state. This article explores what constitutes healthcare policy, uncovers the new developments in 2024, and provides an in-depth examination of how these changes may affect individuals across different states.
Defining US Healthcare Policy
US healthcare policy encompasses the statutes, rulings, and norms that govern the provision, expense, and availability of medical care. This includes federal schemes like Medicare and Medicaid, state-specific initiatives, and private insurance mandates. These policies aim to ensure fair healthcare access, enhance public health, and control expenditures efficiently. The healthcare system faces many challenges, including healthcare system costs and private insurance coverage.
However, given the substantial autonomy states have, the effects of healthcare policy modifications can greatly vary. Initiatives that expand Medicaid, adjust subsidies, or alter insurance criteria often result in different outcomes for Americans based on their location amid public health systems and fragmented health systems.
Innovations in 2024
Transformative Changes in 2024 Healthcare Policies
Enhancement of Behavioral and Mental Health Support: Amplified federal assistance for mental health resources will cascade to state health care facilities, allowing broader programs and fresh ventures.
Medicaid Growth Adjustments: Various states have enlarged Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), with new strategies to boost participation or mitigate coverage lapses. Some states also introduce work mandates for qualification. This demonstrates the importance of government-subsidized plans.
Prescription Drug Price Ceilings: Federally imposed limits on specific prescription drugs begin in 2024, targeting reductions in expenses for the elderly and economically challenged households.
Propagation of Telehealth: Additional federal investment in telehealth systems aims to enhance healthcare delivery, particularly in rural zones. States now face decisions on fund allocation to optimize healthcare system efficiency.
Revisions in Insurance Marketplaces: Enhanced grants for middle-income families on both state and federal insurance platforms will impact cost-effectiveness and enrollment figures in contrast to universal healthcare coverage.
Impacts of Changes Across States
The consequences of these healthcare adjustments hinge on factors like pre-existing healthcare setups, political scenarios, and demographic characteristics. Below is an analysis of how 2024’s healthcare reforms might shape lives state by state amid potential healthcare access disparities.
Northeast Region
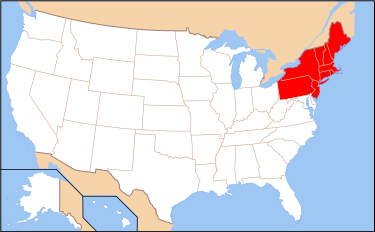
New York
Expansion of Medicaid: Increased Medicaid resources permit wider coverage, notably benefiting undocumented immigrants and low-income groups, which may influence the healthcare system comparison.
Capped Prescription Drug Prices: Significant savings anticipated for the elderly, with a forecasted 30% reduction in out-of-pocket expenses.
Massachusetts
Insurance Market Strategies: The state leverages federal support to boost marketplace participants, focusing on the uninsured middle-income segment, showcasing differences in healthcare financing mechanisms.
Mental Health Enhancement: New funding broadens access to therapy and crisis intervention facilities, underscoring the need for improved healthcare system effectiveness.
Pennsylvania
Telehealth Advancements: Initiatives target rural districts, striving to close healthcare access voids and aiming for higher healthcare system effectiveness.
South Region
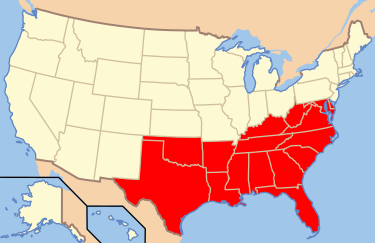
Florida
Medicaid Modifications: The state remains hesitant towards full Medicaid expansion yet introduces partial revisions, influencing eligibility for over half a million residents. Non-profit insurers may play a role in this adjustment.
Telehealth Allocation: Capital directed towards urban locales, leaving rural sectors less served amid healthcare policy reforms.
Texas
Imposed Work Requirements: Newly enacted Medicaid work conditions could restrict access for at-risk demographics, pointing to healthcare access disparities.
Prescription Price Regulations: Positive effects expected, particularly for the aged population, yet concerns persist over access for the uninsured.
Georgia
Behavioral Health Investments: Expanded funding supports new mental health projects in schools and community hubs, contributing to broader health care delivery.
Midwest Region
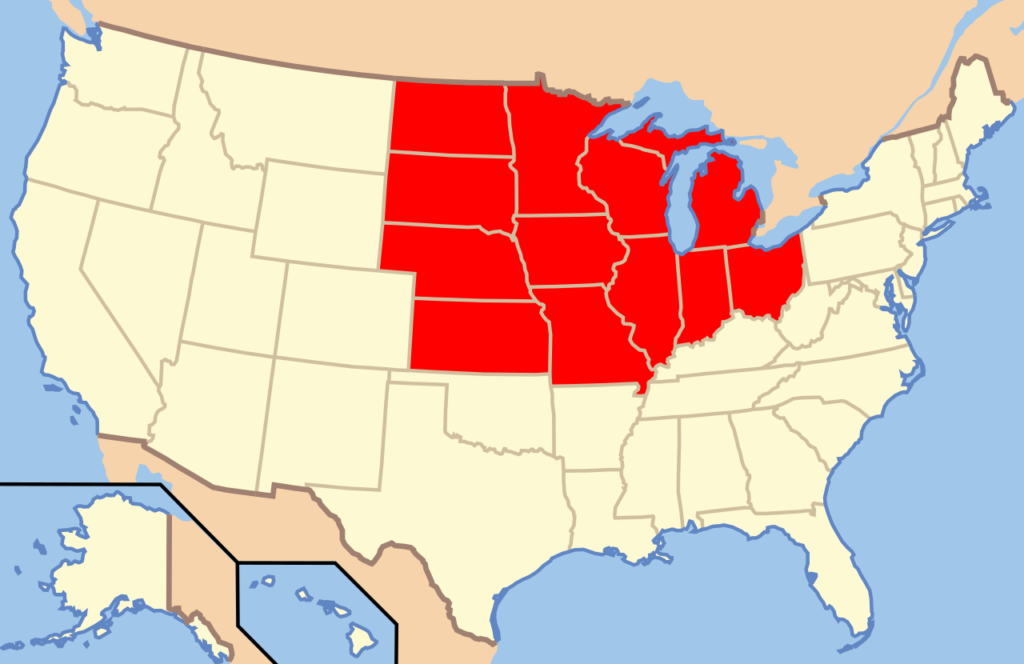
Ohio
Prescription Drug Reductions: Elderly residents benefit significantly from an anticipated $100M savings across the state, affecting healthcare system providers.
Telehealth Strengthening: New rural health initiatives enhance specialist access through telemedicine, improving healthcare system effectiveness.
Michigan
Medicaid Extension: Expanded eligibility boosts coverage for an additional 150,000 residents, highlighting the role of government-subsidized plans.
Marketplace Grant Improvements: Enrollment rates increase due to greater affordability within the healthcare system.
Illinois
Mental Health Emphasis: Resources focus on opioid crisis interventions, establishing more rehabilitation and counseling centers, essential for public health systems.
West Region
California
Inclusive Reform: Comprehensive adoption of federal policies ensures maximum benefits, including affordable drug pricing and expanded Medicaid, offering a unique perspective in healthcare system comparison.
Mental Health Surge: Notable funding influx creates new community wellness initiatives, enhancing health care facilities.
Washington
Telehealth Innovation: Statewide infrastructure advancements set a benchmark for rural healthcare access, showcasing healthcare policy reforms.
Capped Drug Costs: Substantial savings for patients with chronic conditions emphasize the need for a fair healthcare financing mechanism.
Arizona
Medicaid Enhancements: Federal incentives aid Medicaid expansion, though gaps remain in certain rural locales; this highlights fragmented health systems.
Behavioral Health Support: Increased funding targets underserved populations, reducing wait times for services, crucial for healthcare system efficiency.
Translating Changes to Daily Life
The 2024 healthcare reforms have considerable implications for Americans. In states like New York and California, residents observe state-specific policy outcomes through heightened healthcare access and affordability. In contrast, in states such as Texas and Florida, policy restrictions persist, underscoring existing inequalities.
Closing Thoughts
The analysis of 2024 healthcare policy changes underscores the fragmented nature of the US healthcare system. While some states advance boldly toward improved access and affordability, others face challenges posed by political or logistical barriers.
Understanding healthcare policy implications across the US is crucial for advocating reforms that benefit all Americans. Whether residing in New York or Texas, these transformations will shape the accessibility and affordability of healthcare in the future. By staying informed, citizens can support state policies that address their needs.ting reforms that work for all Americans. Whether you live in New York or Texas, these changes will shape how you access and afford healthcare in the years to come. By staying informed, citizens can push for state-level policies that prioritize their needs.
In our other blog article we have discussed the induction of Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a known vaccine skeptic, into Donald Trump’s circle of health advisors raises alarms about opposition to science-backed public health measures. Read the full article here Potential Changes in Health Care Reforms 2024 under the Trump Administration
External Links
Federal websites (e.g., Healthcare.gov)
Research studies (e.g., Kaiser Family Foundation reports)